The AI chip market, once the domain of a few stalwarts, now brims with innovation. This transformation signals a new era. This semiconductor space is suddenly exploding with innovation, fueled by both tech giants and daring startups. The AI chip race is on, and the stakes couldn’t be higher.
After 17 years deep in the trenches of the semiconductor industry at Qualcomm, I’ve witnessed firsthand the cycles of booms and busts that have churned this landscape. But never before have I seen the AI chip market brimming with such relentless innovation, exploding with new players and possibilities.
In this piece, I will survey the battlefield and profile the key figures shaping the AI chip renaissance, exploring their distinct weapons and vulnerabilities. By examining the technology, business models, and competitive conditions these players operate under, we can spot strategic frameworks that reveal how this exhilarating market will likely unfold. The stakes could not be higher, with the very future of AI and computing hanging in the balance. Let’s dive in.
Specialization vs. Versatility:
As we examine the competitive landscape of the AI chip market, a key strategic dichotomy emerges between specialization and versatility. Companies like Google have chosen the path of specialization with their TPUs, achieving remarkable efficiency for specific machine learning tasks within their vast data centers. This specialization offers them unparalleled performance in these domains but may limit their reach into broader markets. On the other hand, entities such as Nvidia, Qualcomm and AMD showcase versatility with chips that cater to a vast spectrum of applications, from mobile devices to data centers. This versatility could be the deciding factor in capturing the larger share of a diversified AI chip market.
Ecosystem Power:
The power of an ecosystem cannot be overstated in the AI chip arena. Robust software, cloud services, and strategic partnerships form the backbone of a successful AI chip offering. Companies like Microsoft and Amazon are capitalizing on their expansive cloud infrastructure to create compelling value propositions for their AI chips. By integrating their silicon solutions with cloud services, they are not just selling a chip; they are providing a holistic solution that promises seamless performance and scalability. This ecosystem power is a formidable force, one that could potentially tilt the scales in favor of those who can effectively merge hardware prowess with software and service mastery.
Geopolitical Impact Analysis:
In the intricate dance of global commerce, geopolitical factors play a leading role. The AI chip market is not immune to these forces, with international policies and tensions significantly impacting supply chains and market accessibility. Companies like Huawei find themselves at the epicenter of such challenges, where geopolitical dynamics can dictate the pace and trajectory of market penetration. Understanding these geopolitical influences is crucial for predicting how the market landscape may shift, and which companies may find their growth impeded or facilitated by forces beyond the market itself.
GPU Titans
Nvidia:
- Nvidia, known for its advanced GPUs like the H100, is a leader. Its next venture, the H200 chip, promises further advancements. Nvidia’s strength lies in high-performance GPUs, crucial for complex AI tasks.
- Strength:Unmatched high-performance GPUs for complex AI tasks.
- Achilles’ heel: Power-hungry design, limiting potential applications.
- Top Customers: Major cloud service providers, automotive companies, gaming industry.
- Growth Prospects: Continued dominance in AI and gaming, potential expansion into automotive AI.
- Unique Challenge: Balancing power consumption with performance.
AMD:
- Radeon Instinct MI300 boasts impressive performance at lower power consumption.
- Strength: Competitive pricing and power efficiency.
- Achilles’ heel: Smaller ecosystem compared to Nvidia.
- Top Customers: Cloud service providers, PC manufacturers, gaming console makers.
- Growth Prospects: Gaining market share in cloud and gaming sectors, expanding into AI and machine learning.
- Unique Challenge: Expanding its ecosystem to rival Nvidia’s comprehensive offerings.
Qualcomm:
- Qualcomm holds a dominant position in the mobile SoC market, giving them a strong foundation for AI integration. Their Snapdragon chips are specifically designed for on-device AI processing, crucial for mobile applications and the Internet of Things (IoT).
- Strengths: They offer a range of AI-enabled chips catering to various segments, from smartphones and wearables to automotive and robotics. Qualcomm collaborates with leading AI companies and research institutions to stay ahead in the technology curve.
- Achilles’ heels: Nvidia and AMD are increasingly targeting the mobile and edge AI space. While their chips excel in edge AI, they might not be able to compete with Nvidia’s dominance in complex AI tasks requiring massive compute power. Their AI capabilities are somewhat tied to collaborations with other companies,potentially impacting flexibility and control.
- Top Customers: Smartphone manufacturers, automotive industry, IoT device makers.
- Growth Prospects: Dominance in mobile AI, expansion into automotive and IoT sectors.
- Unique Challenge: Facing intense competition in mobile AI from Nvidia and AMD.
Huawei:
- Huawei’s Ascend 910B focuses on AI chip market consolidation. Huawei aims to leverage its existing technology base. However, geopolitical factors could impact its market reach.
- Strengths: Existing technology base, strong domestic market presence, competitive pricing.
- Achilles’ heel: Geopolitical tensions impacting international reach, potential reliance on specific technologies/suppliers.
- Top Customers: Telecom operators, enterprise clients in China, consumer electronics segment.
- Growth Prospects: Growth in domestic market, expansion in IoT and cloud computing.
- Unique Challenge: Navigating geopolitical challenges, diversifying technology suppliers
Cloud Crusaders
Microsoft:
- Microsoft’s Azure Maia 100 AI chip aims to reduce external dependencies. By integrating chips directly with its cloud services, Microsoft strengthens its ecosystem.
- Strength: Tight integration with cloud services.
- Achilles’ heel: Needs to establish hardware prowess against seasoned players.
- Top Customers: Azure cloud service users, enterprise clients.
- Growth Prospects: Deepening integration of AI chips with cloud services, expanding Azure’s market share.
- Unique Challenge: Establishing a reputation in hardware against established semiconductor giants.
Amazon:
- Amazon’s Trainium chip bolsters its AWS cloud services. The Trainium focuses on machine learning, enhancing Amazon’s AI capabilities. However, Amazon’s chips are primarily cloud-centric.
- Strength: Seamless integration with cloud offering.
- Achilles’ heel: Limited to cloud applications, similar to Google’s TPUs.
- Top Customers: AWS cloud service users, large-scale enterprise clients.
- Growth Prospects: Enhancing AWS’s AI capabilities, expanding in cloud-based AI services.
- Unique Challenge: Limited scope due to focus on cloud-specific applications.
In-House Innovators
Meta:
- MTIA and upcoming Artemis chips boast efficiency tailored for Meta’s specific needs. These chips are tailored for AI applications, optimizing efficiency.
- Strength: Optimized for internal use cases.
- Achilles’ heel: Limited market presence and broader application uncertainty. Meta’s chips are less proven in the broader market, a potential hurdle.
- Top Customers: Primarily internal use for social media, VR, and AR applications.
- Growth Prospects: Improving efficiency and performance of Meta’s platforms.
- Unique Challenge: Proving the broader market viability of its chips outside Meta’s ecosystem.
Google:
- Google’s Tensor Processing Units (TPUs) are at the forefront of machine learning acceleration. TPUs excel at accelerating machine learning tasks within Google’s massive data centers. TPUs are tailored for Google’s data centers, a strength and limitation. Their specialized nature restricts broader applications.
- Strength: Powerful for specific use cases.
- Achilles’ heel: Specialization restricts broader adoption.
- Top Customers: Internal use within Google’s services like Search, YouTube, and Cloud.
- Growth Prospects: Enhancing AI capabilities of Google’s products, potential expansion in cloud services.
- Unique Challenge: Limited application scope due to specialization for internal use.
Rising Stars
Groq:
- Groq’s innovative Language Processing Unit (LPU) redefines AI language models. Its Tensor Streaming Processor (TSP) architecture represent a paradigm shift in language processing, offering low latency and power consumption. With speeds up to 500 tokens per second, it outperforms traditional GPUs. Groq’s LPU provides a faster response for AI applications but faces the challenge of market adoption against GPU giants.
- Strength: Innovative technology exceeding GPU performance.
- Achilles’ heel: Needs to overcome market dominance of GPUs.
- Top Customers: Potential clients in data centers, AI research, and high-performance computing.
- Growth Prospects: Market adoption in sectors requiring high-speed language processing.
- Unique Challenge: Gaining market traction against traditional GPU players.
SoftBank’s Izanagi:
- SoftBank’s Izanagi project marks its entry into the AI chip market. With significant investment, SoftBank aims to compete with Nvidia. The challenge lies in establishing a foothold in a market with entrenched leaders.
- Strength:Financial backing and potential for disruption.
- Achilles’ heel: Needs to carve a niche against established players.
- Top Customers: Yet to be established, potential in various AI application sectors.
- Growth Prospects: Disrupting existing market with innovative technology.
- Unique Challenge: Establishing a market presence and customer base.
Sam Altman’s Ambitious Vision:
- OpenAI’s Sam Altman seeks a massive investment for a chip-making venture. The goal is to develop competitive AI chips. Altman’s vision is bold, but the path to success is fraught with challenges, especially against established players.
- Strengths: Bold vision, potential for disruption, access to talent and resources through OpenAI.
- Achilles’ heel: Unproven technology, fierce competition, securing massive investment amidst economic uncertainty.
- Top Customers: Potential in various sectors leveraging AI technology.
- Growth Prospects: Pioneering in new AI chip technologies, leveraging OpenAI’s research.
- Unique Challenge: Moving from vision to viable product amidst intense competition.
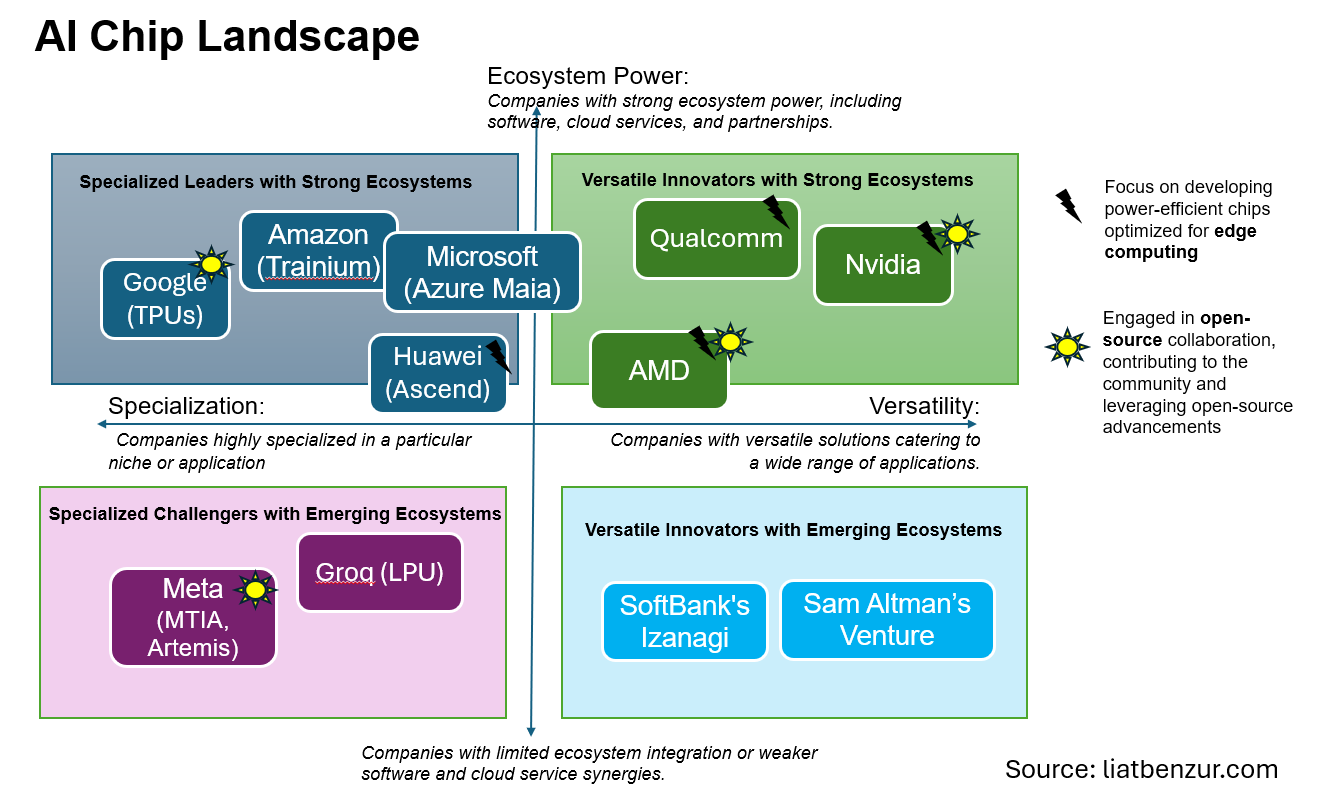
Strategic Framework for Assessing This Chip Landscape
Below is a matrix positioning the various AI chip competitors discussed above. You will notice the companies are separated across the following areas of differentiation:
- Specialization vs. Versatility: Striking the right balance between catering to specific needs and offering broader appeal is crucial.
- Ecosystem Power: Integrating chips with robust software and cloud services creates a compelling value proposition.
- Performance at the Edge: Power-efficient chips optimized for edge computing hold immense potential.
- Openness vs. Control: Balancing proprietary technology with open-source collaboration can foster innovation and adoption.
Performance at the Edge:
In the context of the AI chip market, the edge represents the frontiers of computational performance—where the processing is done close to the source of data. Here, the efficiency of the chip is paramount. Companies like Nvidia, with their H200 chip, and AMD, with the Radeon Instinct MI300, are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in terms of power-efficient design. This emphasis on performance at the edge is pivotal, especially in applications where latency and power consumption are critical. As we transition to a world ever more reliant on IoT and mobile devices, the ability to deliver high-performance computing in a power-efficient manner will become a key battleground for these tech giants.
Innovative Business Models:
As the technological arms race accelerates, so does the innovation in business models within the AI chip sector. Some companies are breaking the mold with ‘chip-as-a-service’ models, offering AI processing power on a subscription basis, thus democratizing access to advanced AI capabilities. Collaborative ventures are also emerging, where AI chip firms are joining forces with other tech sectors to create integrated solutions that transcend traditional market boundaries. These innovative business models are as much a part of the AI chip renaissance as the silicon itself, and they will play a pivotal role in determining how these technologies are adopted and monetized.
Integration with Emerging Technologies:
As the AI chip market evolves, the integration with emerging technologies becomes a game-changer. Companies are exploring synergies with quantum computing, which promises to disrupt the very fabric of processing power and data analysis. Neuromorphic computing is also on the horizon, with its potential to create chips that emulate the human brain’s efficiency and decision-making processes. Furthermore, the integration of AI chips into blockchain applications heralds a new era of secure and intelligent transaction management. These technological frontiers offer fertile ground for innovation, and companies that can effectively harness these synergies may well define the future of the AI chip industry.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact:
In an era where environmental considerations are paramount, the AI chip industry is under scrutiny for its sustainability practices. Manufacturing chips is resource-intensive, and operations consume significant energy. Therefore, companies are now tasked with designing chips that not only push the envelope in performance but also in environmental friendliness. From utilizing renewable energy sources in manufacturing plants to designing chips that require less power, these strategies are crucial for the long-term viability of AI technologies and their acceptance by an eco-conscious public.
Here’s an overview of how each company might be approaching these challenges:
- Nvidia: Nvidia could be focusing on improving the energy efficiency of their GPUs, as these chips are traditionally power-hungry. Nvidia might also be focusing on the entire lifecycle of its AI chips, from design to disposal. The company could be investing in more energy-efficient architectures and exploring advanced materials that reduce the ecological footprint during manufacturing. Furthermore, Nvidia might be collaborating with environmental organizations to offset carbon emissions and support renewable energy projects.
- AMD: As a competitor in the energy-efficient processor market, AMD may be stepping up its efforts by employing precision manufacturing techniques that reduce material waste. The company could also be integrating low-power design features into its AI chips, contributing to reduced energy consumption in end-user applications.
- Qualcomm: Qualcomm’s chips are prevalent in mobile devices, which require energy efficiency. The company may emphasize reducing power consumption in operation, and it could be utilizing eco-friendly packaging and responsible sourcing for materials. Qualcomm’s approach to sustainability may include deploying AI itself to optimize manufacturing processes, thereby reducing energy usage and improving yield. The company could also be focusing on the recyclability of its chips and reducing toxic materials in its products, adhering to stringent international environmental standards.
- Huawei: Huawei could be leveraging its significant presence in China to advance sustainability in its supply chain, possibly using more renewable energy in its operations and focusing on energy-efficient chip designs.It might also be leveraging its AI technology to create smart manufacturing systems that conserve energy and reduce emissions. In response to geopolitical pressures, the company could be doubling down on self-reliance, sourcing materials locally to reduce transportation-related carbon footprint and promoting a circular economy within its supply chain.
-
- Microsoft (Azure Maia): As a company with a broad commitment to sustainability, Microsoft might integrate those principles into the design and production of the Azure Maia chip, potentially focusing on reducing waste and improving the energy efficiency of data centers where the chips are used. Microsoft’s Azure Maia chips could be designed with the cloud in mind, optimizing data center operations for energy savings. The company might be working towards making its data centers more sustainable through advanced cooling systems and using AI-powered algorithms to manage data center efficiency.
- Amazon (Trainium): Amazon Web Services has made commitments to renewable energy usage. With AWS’s global infrastructure, Amazon’s Trainium chips could be designed to optimize workload efficiency, thereby reducing the overall energy demand of cloud services. Amazon may be pursuing ambitious goals to power its operations with 100% renewable energy, influencing the production and operation of its Trainium chips.
- Google (TPUs): Google has been a leader in corporate renewable energy purchases. This commitment likely extends to their TPU manufacturing processes, with an emphasis on operational efficiency within Google’s data centers to reduce the overall environmental impact. Google could be integrating environmental considerations into its TPUs by reducing power usage at scale across its services. The company might be focusing on the reuse and repurposing of computing hardware, including TPUs, and pushing for the use of sustainable energy in its data centers where TPUs are extensively used.
- Meta (MTIA, Artemis): Meta’s AI chips, such as MTIA and Artemis, might be part of the company’s broader initiative to reduce its carbon footprint. This could involve designing chips that require less energy for AI processing tasks, thereby contributing to the energy efficiency of their vast array of services.
- Groq (LPU): As a newer company, Groq has the opportunity to build sustainability into its operations from the ground up. This could involve innovative cooling technologies for their processors and the use of renewable energy in their offices and data centers. Groq could be prioritizing sustainability by utilizing chip designs that maximize computational throughput per watt, effectively lowering power requirements. The company might also be pioneering new methods of chip fabrication that are less polluting and more energy-efficient.
- SoftBank’s Izanagi: SoftBank might be investing in sustainable AI chip development by funding startups that are focusing on novel, energy-efficient chip architectures and environmentally friendly manufacturing techniques. SoftBank’s Izanagi project might be incorporating sustainability in its blueprint by investing in technologies that extend the lifespan of AI chips. SoftBank could also be supporting initiatives that promote the use of renewable energy in semiconductor manufacturing, setting a new standard for the industry.
- Sam Altman’s Venture: Given Sam Altman’s ties with OpenAI, there could be a strong focus on creating AI chips that are not only cutting-edge in terms of performance but also set new standards for sustainability in both manufacture and operation. The chip-making venture spearheaded by Sam Altman could be built on the foundation of sustainability, with a focus on developing AI chips that not only perform well but also have a minimal environmental impact. This might include innovative cooling technologies that reduce energy use and designing chips that can be easily updated or recycled to extend their usable life.
For each of these companies, sustainability in the AI chip industry could involve a variety of strategies: investing in renewable energy, improving the efficiency of the chips themselves, reducing waste and hazardous materials in production, establishing recycling programs for old equipment, and designing data centers that minimize energy consumption.
Conclusion
We stand at the precipice of a new technological epoch. The AI chip market has burgeoned from a niche corner of the semiconductor world into a bustling arena of innovation, with a pantheon of tech titans and nimble startups vying for supremacy.
As the AI chips grow smarter, greener, and more integrated into the very fabric of our lives, one thing remains clear: the renaissance of semiconductors is far from just a revival—it’s a revolution. A revolution that’s not only bringing ‘semiconductor sexy back’ but also charting a course for a future where technology and sustainability must go hand-in-hand.
The race for AI chip supremacy isn’t just about who crosses the finish line first; it’s about who does so responsibly, sustainably, and in a way that benefits all of humanity. The stakes are indeed high, and the world watches with bated breath.