As a board director, are you prepared to navigate the complex landscape of AI risk management? The consequences of failing to effectively govern AI can be severe, from reputational damage to legal liabilities.
But where do you start? This essential guide provides a comprehensive playbook for boards to successfully oversee responsible AI development and deployment.
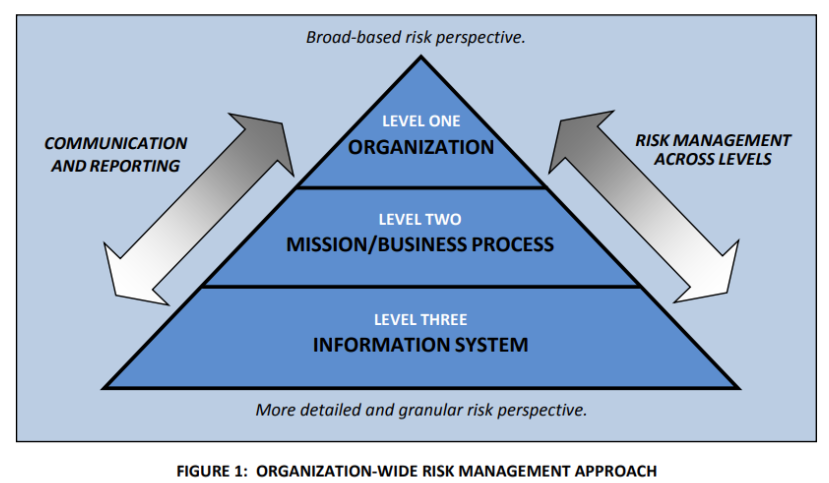
In this blog post, I present a simplified, step-by-step playbook for boards to establish and maintain effective AI governance. This leverages the NIST AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF). The NIST AI RMF is a comprehensive set of guidelines designed to help organizations manage the risks associated with AI systems. Released by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology in January 2023, the framework provides a structured approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks throughout the AI lifecycle. The AI RMF emphasizes key characteristics such as transparency, fairness, accountability, and reliability, making it an essential tool for organizations seeking to develop and deploy AI systems responsibly.
Each step includes key questions board members should ask, along with guidance on what to look for in the answers and which frameworks to leverage for assessment. By following these best practices, you can foster a culture of responsible AI, build trust with stakeholders, and mitigate potential harms throughout the AI lifecycle.
Step 1: Map the AI System Lifecycle and Impacts
Begin by developing a comprehensive understanding of each AI system’s goals, scope, and potential impacts.
Board members should ask:
– What are the intended use cases, benefits, and risks of each AI system?
– How are we engaging diverse stakeholders to identify potential impacts?
– What processes are in place to monitor for unexpected impacts?
What to look for:
- Clear documentation of AI system objectives, methods, and lifecycle stages
- Evidence of broad stakeholder engagement, including impacted communities
- Processes for ongoing impact monitoring, including mechanisms for flagging unexpected issues
Frameworks to utilize:
- AI Lifecycle Frameworks (e.g., IEEE 7000-2021, AI RMF)
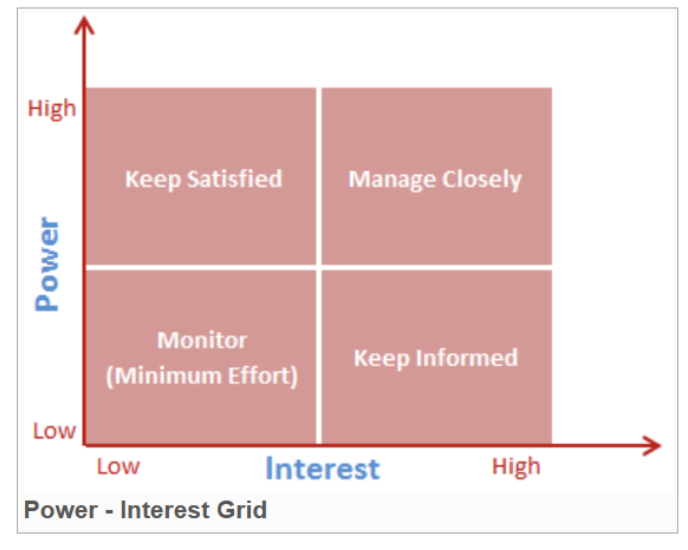
- Stakeholder Analysis Tools (e.g., Stakeholder Mapping, Power-Interest Grid)
Step 2: Establish a Robust AI Governance Framework
Create a strong foundation for AI risk management by establishing clear policies, guidelines, and responsibilities.
Board members should ask:
– Do we have comprehensive AI ethics policies and training programs?
– How are AI governance responsibilities integrated into organizational roles?
– Is there a clear inventory of our AI systems and their key characteristics?
What to look for:
- AI ethics policies aligned with organizational values and industry best practices
- Role-based AI governance responsibilities and training requirements
- Comprehensive AI system inventory with risk classifications and ownership details
Frameworks to utilize:
- AI Ethics Frameworks (e.g., OECD AI Principles, IEEE Ethically Aligned Design)
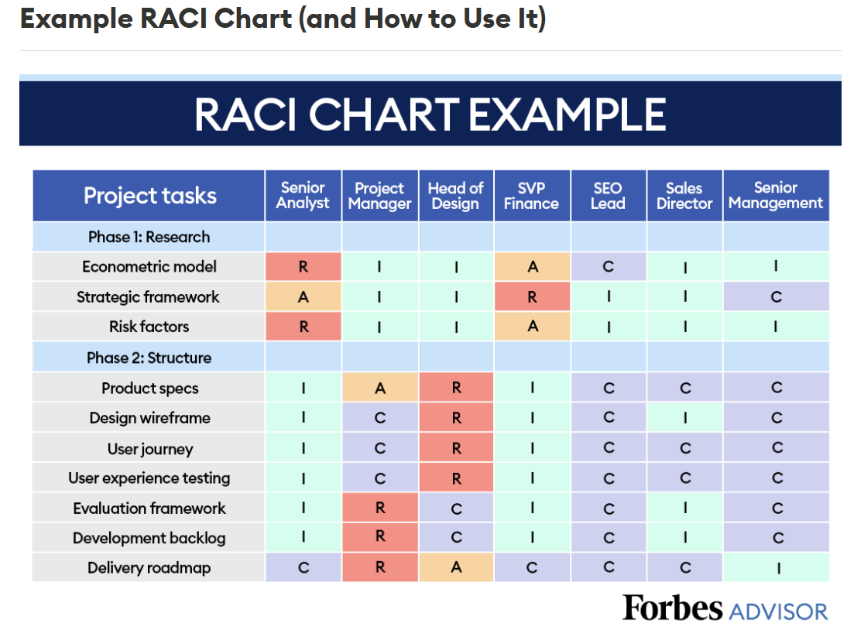
- Responsibility Assignment Matrices (e.g., RACI Matrix)
Step 3: Implement Comprehensive Risk Assessment Processes
Ensure that rigorous risk assessment processes are in place for all AI systems.
Board members should ask:
– What risk assessment methods, metrics, and datasets are being used?
– How often are key risk areas like fairness and security evaluated?
– Are we using standardized documentation like Model Cards and Datasheets?
What to look for:
- Use of multiple risk assessment methods, including technical audits and impact assessments
- Regular testing for fairness, privacy, security, and other key risk areas
- Standardized documentation providing transparency on models and datasets
Frameworks to utilize:
- Risk Assessment Frameworks (e.g., NIST AI Risk Management Framework, ISO 31000)
- Model Documentation Templates (e.g., Model Cards, Datasheets for Datasets)
Step 4: Prioritize Transparency and Accountability
Build trust in your AI systems by prioritizing transparency and accountability.
Board members should ask:
– How are we communicating AI system limitations and risk controls?
– What appeal and redress processes are available to impacted stakeholders?
– Are we regularly reporting on our AI governance practices and outcomes?
What to look for:
- Clear, public communication of AI system capabilities, limitations, and risk mitigation measures
- Established processes for stakeholders to appeal AI decisions and seek redress
- Regular, transparent reporting on AI governance practices and performance indicators
Frameworks to utilize:
- Transparency Reporting Frameworks (e.g., AI Transparency Reporting)
- Algorithmic Accountability Frameworks (e.g., Algorithmic Impact Assessments)
Step 5: Develop Proactive Risk Mitigation and Response Plans
Minimize potential harms by developing proactive risk mitigation and response measures.
Board members should ask:
– What are our risk mitigation plans for high-priority AI risks?
– How are we justifying risk acceptance decisions?
– What incident response protocols do we have in place for AI issues?
What to look for:
- Detailed risk mitigation plans addressing identified high-priority risks
- Documented justifications for risk acceptance decisions, considering potential impacts
- Comprehensive incident response plans, including escalation protocols and public communication strategies
Frameworks to utilize:
- Risk Mitigation Planning Frameworks (e.g., NIST SP 800-37)
- Incident Response Frameworks (e.g., NIST Computer Security Incident Handling Guide)
Step 6: Conduct Rigorous Pre-Deployment Checks
Before deploying any AI system, conduct thorough pre-deployment checks.
Board members should ask:
– Have we verified the AI system’s reliability, performance, and standards adherence?
– What conditions would prevent us from deploying the system?
– Do accountable executives sign off before any AI system deployment?
What to look for:
- Comprehensive testing results demonstrating system reliability and performance
- Clear go/no-go criteria for AI system deployment decisions
- Formal executive sign-off processes for AI system deployments
Frameworks to utilize:
- Pre-Deployment Checklists (customized based on organizational requirements)
- Quality Assurance and Testing Frameworks (e.g., ISO 25010)
Step 7: Monitor AI Systems Post-Deployment
Ensure ongoing monitoring of AI systems after deployment.
Board members should ask:
– What post-deployment monitoring is conducted on AI system behavior and impacts?
– How are we assessing the long-term performance and value of our AI systems?
– Under what conditions would we decommission or replace an AI system?
What to look for:
- Continuous monitoring processes tracking AI system performance and impacts
- Regular assessments of AI system value and alignment with intended objectives
- Defined criteria and protocols for AI system decommissioning or replacement
Frameworks to utilize:
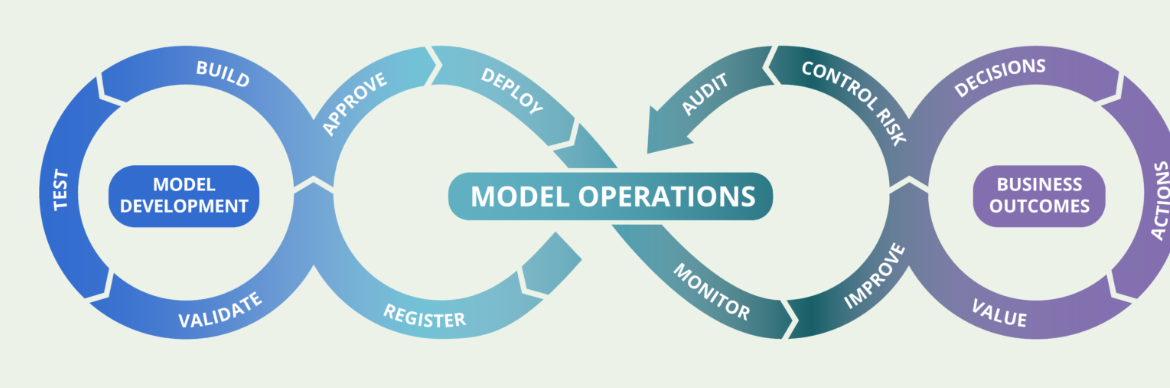
- Post-Deployment Monitoring Frameworks (e.g., ModelOps, ML Observability)
- Value Realization Frameworks (e.g., Benefits Realization Management)
Step 8: Engage Diverse Stakeholders
Proactively engage diverse stakeholders, including vulnerable groups, to understand and address AI impacts.
Board members should ask:
– How are we engaging internal and external stakeholders impacted by AI?
– What processes are in place to incorporate stakeholder feedback?
– Are we transparently disclosing our stakeholder engagement outcomes?
What to look for:
- Inclusive stakeholder engagement strategies, with an emphasis on impacted and vulnerable groups
- Established feedback loops to incorporate stakeholder input into AI system improvements
- Transparent communication of stakeholder engagement activities and resulting actions
Frameworks to utilize:
- Stakeholder Engagement Frameworks (e.g., AA1000 Stakeholder Engagement Standard)
- Participatory Design Frameworks (e.g., Co-Design, Community-Based System Dynamics)
Step 9: Continuously Review and Enhance AI Governance
Regularly assess the effectiveness of your AI governance practices and adapt based on evolving best practices and changing risks.
Board members should ask:
– How are we assessing the effectiveness of our AI governance practices?
– What processes are in place to adapt our governance to new risks and best practices?
– How are we disclosing the results of our governance reviews and enhancements?
What to look for:
- Regular audits and assessments of AI governance practices and outcomes
- Proactive monitoring of emerging AI risks and governance best practices
- Transparent reporting on governance review findings and improvement actions
Frameworks to utilize:
- Governance Maturity Models (e.g., Responsible AI Maturity Model)
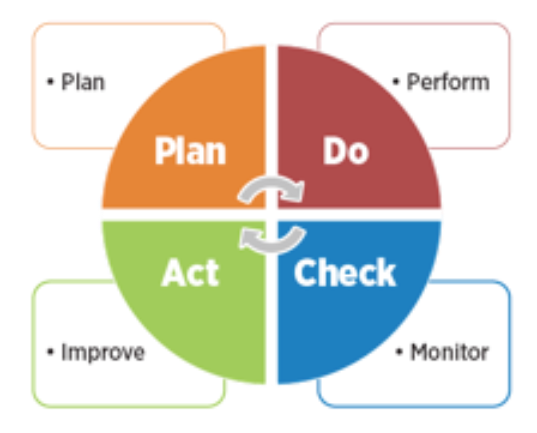
- Continuous Improvement Frameworks (e.g., Plan-Do-Check-Act)
Step 10: Provide Board Oversight and Accountability
Ensure your board has the necessary AI ethics expertise and oversight structures in place.
Board members should ask:
– Do we have sufficient AI ethics expertise on the board?
– Is management regularly reporting on AI governance to the board?
– How are we holding executives accountable for AI system outcomes and risk management?
What to look for:
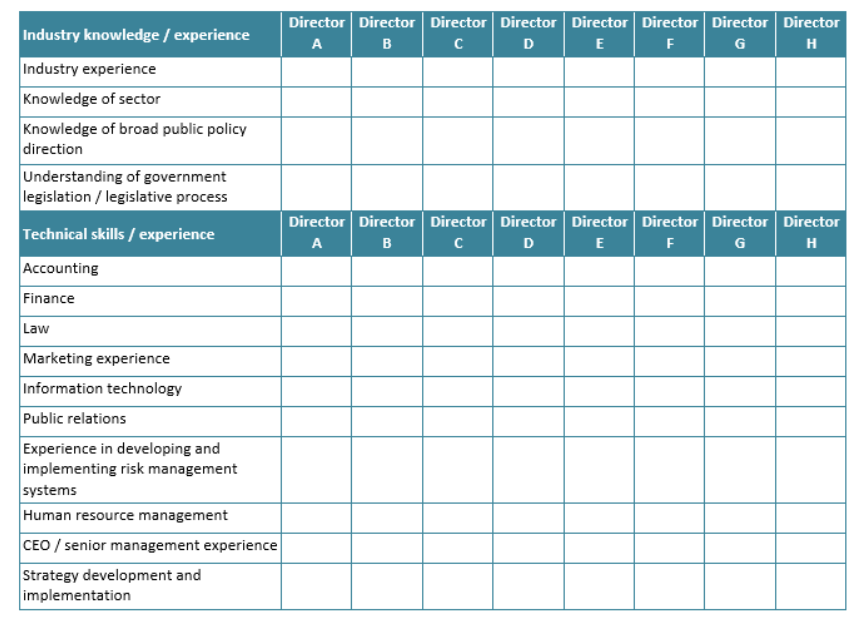
- Board composition that includes members with AI ethics and governance expertise
- Regular, comprehensive AI governance reporting from management to the board
- Clear accountability mechanisms for executives responsible for AI system outcomes
Frameworks to utilize:
- Board Skill Matrix (to assess and develop necessary AI governance competencies)
- AI Governance Reporting Templates (to ensure consistent, comprehensive reporting)
By asking these critical questions at each step of the AI governance process, board directors can fulfill their responsibility to provide effective oversight of AI development and deployment. Implementing this playbook positions boards to proactively mitigate AI risks, drive responsible innovation, and safeguard the long-term interests of their organizations and stakeholders. As AI continues to advance, embracing responsible governance practices will be a defining factor in building trust and achieving sustainable success in the age of AI.
As you embark on the journey of responsible AI governance, remember that knowledge alone is not enough. Take action today to assess your organization’s AI governance practices, engage with stakeholders, and stay informed about emerging trends and best practices. Together, we can shape a future where AI drives innovation responsibly and ethically.